Loperamide Hydrochloride, Discovery, Action, Effective Uses, Side effects, Precautions, Dosage and 15 Brands.
- June 14, 2024
- 0 Likes
- 63 Views
- 0 Comments
Introduction
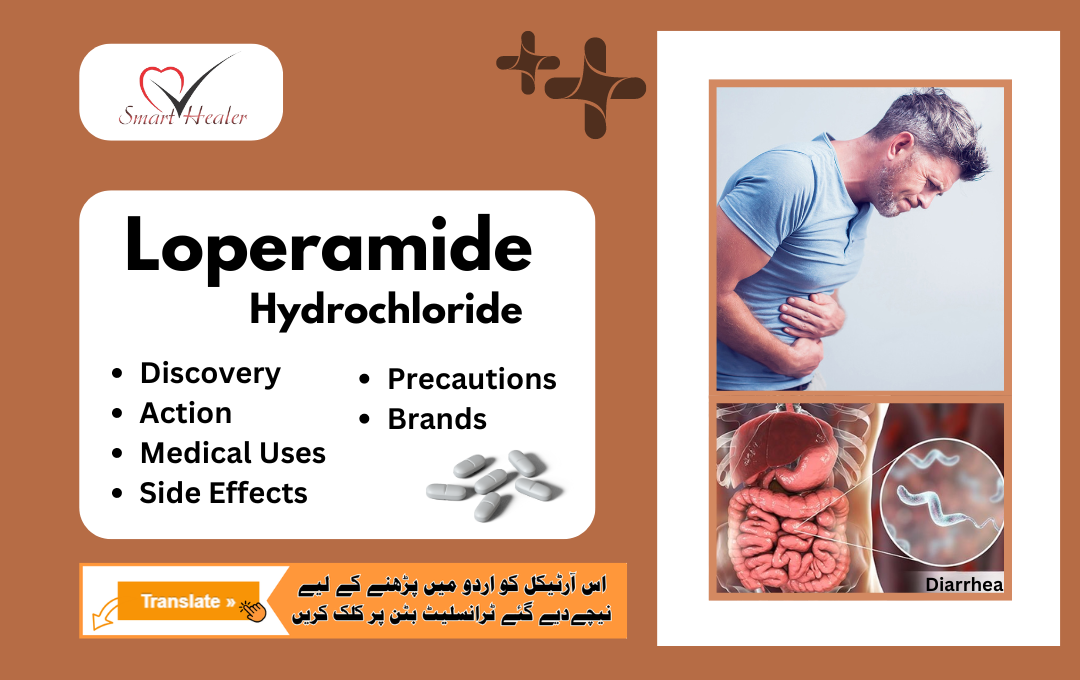
Loperamide hydrochloride, commonly known as Imodium, is a trusted antidiarrheal medication that plays a vital role in managing diarrhea. As an opioid receptor agonist, it effectively reduces the frequency of diarrhea, providing relief for patients with irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, short bowel syndrome, Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis.
It is available in various formulations, including tablets, capsules, and liquid solutions, loperamide hydrochloride offers flexible treatment options for individuals seeking relief from diarrhea symptoms, Whether it’s a sudden bout of traveler’s diarrhea or chronic gastrointestinal problems.
Discovery of Loperamide Hydrochloride
The discovery of loperamide hydrochloride is a significant milestone in the field of gastroenterology and pharmacology. it was developed in the early 1970s, loperamide was synthesized by researchers at Janssen Pharmaceutica, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson. The discovery was led by Dr. Paul Janssen, a renowned Belgian pharmacologist whose contributions to medicine include numerous groundbreaking drugs.
Development and Research
- Background: Before the development of loperamide hydrochloride, there was a pressing need for an effective antidiarrheal medication with minimal central nervous system (CNS) effects. Existing treatments frequently cause sedation or addiction due to opioid-like mechanisms.
- Synthesis: It was synthesized to act specifically on the opioid receptors in the gut, reducing intestinal motility without significant penetration of the blood-brain barrier. This targeted approach reduced the risk of CNS side effects like drowsiness and dependence.
- Clinical Trials: Early clinical trials demonstrated that loperamide was effective in reducing diarrhea symptoms while maintaining a favourable safety profile. These studies confirmed the mechanism of action, which involves slowing intestinal transit while increasing fluid and electrolyte absorption.
Approval and Market Introduction
- Regulatory Approval: Following successful clinical trials, loperamide received approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1976 for the treatment of acute and chronic diarrhea. It was initially available by prescription only.
- Over-the-Counter Availability: Recognizing its safety and effectiveness, the FDA later approved loperamide for over-the-counter (OTC) sale in 1988. This increased availability made it a popular choice for managing diarrhea symptoms worldwide.
Impact on Medicine
- Global Use: Loperamide hydrochloride has since become one of the most widely used antidiarrheal medications globally.Its inclusion on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines highlights its importance to global health.
- Further Research: The success of loperamide has spurred further research into peripherally acting opioids and other gastrointestinal treatments, advancing our understanding and management of digestive disorders.
Mechanism of Action
Loperamide hydrochloride, also known as Imodium, is an effective antidiarrheal medication. It works by acting on the opioid receptors in the intestines to slow down bowel movements and increase the amount of water and electrolytes absorbed by the intestines. A detailed explanation of its mechanism of action is the following:
1. Opioid Receptor Binding
Loperamide binds to the opioid receptors (mu, delta, and kappa) in the intestinal wall, specifically in the circular and longitudinal muscle layers. These receptors are components of the enteric nervous system, which regulates gastrointestinal function.
2. Slowed Intestinal Motility
Activation of opioid receptors by loperamide slows down the movement of food through the intestines. This delay in transit time allows more efficient absorption of water and electrolytes.
3. Increased Water and Electrolyte Absorption
With slower intestinal motility, the intestines have more time to absorb water and electrolytes (such as sodium, potassium, and chloride) from the intestinal lumen into the bloodstream. This process helps to solidify the stool and reduce the frequency of bowel movements.
4. Reduced Intestinal Secretion
Loperamide also reduces the secretion of water and electrolytes into the intestines. This dual action of increasing absorption and reducing secretion helps in managing diarrhea more effectively by maintaining a better fluid balance in the intestines.
5. Relaxation of Intestinal Muscle
Loperamide causes relaxation of the intestinal muscles, reducing spasms and cramps that are commonly associated with diarrhea. This effect contributes to the overall comfort and relief of symptoms for the patient.
Loperamide hydrochloride Medical Uses
Loperamide hydrochloride, marketed under brand names such as Imodium, is widely used to treat various types of diarrhea. Its effectiveness and safety profile make it a valuable medication for both acute and chronic conditions. The primary medical uses of loperamide hydrochloride are as follows:
1. Acute Diarrhea
loperamide hydrochloride is commonly used to treat episodes of acute diarrhea, including:
- Traveler’s Diarrhea: Caused by ingestion of contaminated food or water, often during travel to regions with poor sanitation.
- Viral Gastroenteritis: Also known as stomach flu, caused by viral infections such as norovirus or rotavirus.
Food Poisoning: Resulting from bacterial or toxin contamination of food.
2. Chronic Diarrhea
loperamide hydrochloride is effective in managing chronic diarrhea associated with various conditions, such as:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Loperamide is especially effective for the diarrhea-predominant type (IBS-D), where it reduces bowel movement frequency and improves stool consistency.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD): Including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, it helps control diarrhea symptoms.
3. Diarrhea Associated with Gastrointestinal Disorders
loperamide hydrochloride can be used in conditions where diarrhea is a symptom, such as:
- Microscopic Colitis: Loperamide is used to treat lymphocytic and collagenous colitis by reducing inflammation-induced diarrhea.
- Short Bowel Syndrome: A condition in which a large portion of the small intestine is missing or has been surgically removed, causing malabsorption and diarrhea.
4. Management of Ileostomy and Colostomy Output
Loperamide is used to reduce the volume and frequency of discharge in patients with:
- Ileostomies: Surgical openings created in the ileum to divert waste out of the body.
- Colostomies: Surgical openings created in the colon.
5. Adjunctive Therapy
Loperamide can be used as an adjunct to rehydration therapy in the management of:
- Diarrhea in Children: When used with caution and under medical supervision to prevent dehydration.
- HIV/AIDS: In patients experiencing chronic diarrhea due to opportunistic infections or antiretroviral therapy.
6. Other Uses
- Radiation Enteritis:It is used to treat diarrhea caused by radiation therapy to the abdomen or pelvis.
- Chemotherapy-Induced Diarrhea: As a supportive treatment to manage diarrhea resulting from cancer treatments.
Loperamide hydrochloride Dosage
The dose of loperamide hydrochloride (Imodium) varies according to the type of diarrhea and the patient’s age. Here are some general guidelines for dosing:
Acute Diarrhea in Adults
- Initial Dose: 4 mg (two tablets or capsules) taken immediately after the first loose stool.
- Maintenance Dose: 2 mg (one tablet or capsule) after each subsequent loose stool.
- Maximum Daily Dose: Do not exceed 16 mg per day.
Chronic Diarrhea in Adults
- Initial Dose: Typically starts with 4 mg (two tablets or capsules) per day.
- Maintenance Dose: The dose is adjusted based on individual response and can range from 2 mg to 8 mg per day.
Dosage for Children
- Ages 6-12 years: The initial dose is typically 2 mg (one tablet or capsule) after the first loose stool, with subsequent doses of 1 mg (half a tablet or capsule) after each subsequent loose stool. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 6 mg.
- Ages 2-5 years: The dosage should be determined based on weight and under the guidance of a healthcare provider to ensure appropriate dosing and safety.
Special Considerations
- Elderly Patients: Dosage adjustments may be necessary due to potential changes in metabolism and renal function.
- Patients with Liver Impairment: Use with caution as loperamide is metabolized in the liver; lower initial doses and monitoring may be required.
Administration
- Loperamide is typically taken orally with water, either as tablets, capsules, or liquid formulations.
- It can be taken with or without food.
- Ensure adequate hydration, especially in cases of diarrhea.
Loperamide hydrochloride Side effects
Loperamide hydrochloride (Imodium) is generally well-tolerated when used as directed for the treatment of diarrhea. However, like any medication, it can cause side effects in some individuals. The following are the most common and less common side effects of loperamide.
Common Side Effects
- Constipation: This is the most common side effect due to loperamide’s ability to slow down intestinal motility.
- Nausea: Mild stomach discomfort or nausea may occur, especially at higher doses.
- Abdominal Pain or Cramps: Some individuals may experience mild to moderate abdominal discomfort.
- Dizziness: A feeling of lightheadedness or dizziness may occur in some cases.
- Dry Mouth: Reduced saliva production, leading to a dry sensation in the mouth.
Less Common or Rare Side Effects
- Fatigue or Drowsiness: Although loperamide does not typically cause sedation, some individuals may experience fatigue.
- Headache: Mild headaches have been reported in rare cases.
- Allergic Reactions: Symptoms may include rash, itching, swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, or trouble breathing. Seek immediate medical attention if any allergic reaction occurs.
- Serious Gastrointestinal Effects: In rare cases, serious gastrointestinal effects such as severe constipation, abdominal distension or ileus (intestinal blockage) may occur, particularly with high doses or prolonged use.
Precautions and Warnings
Here are some precautions and warnings for loperamide hydrochloride:
- Heart problems: Loperamide can cause serious heart problems, especially if you take more than the recommended dose.
- Dizziness: It can cause dizziness, tiredness or sleepiness, so be careful when driving, cycling, or operating heavy machinery or tools.
- Alcohol: It’s best not to drink alcohol while you’re taking it, as alcohol can increase the likelihood of having side effects.
- History of bowel disease: Be careful when taking loperamide if you have a history of bowel disease, HIV/AIDS or liver problems.
- Medications: They interact with certain medications, such as antibiotics, antifungals, or blood thinners, that may cause QT prolongation.
- Age: Older adults may be more sensitive to the side effects of it.
- Children: Children is more sensitive to the side effects of loperamide and are at a higher risk for dehydration.
- Maximum dosage: Do not take more than the recommended dose of it. Taking higher doses can cause serious heart problems.
- Duration of treatment: If you buy loperamide from a shop or pharmacy, do not take it for more than 48 hours without talking to a doctor.
Drug Interactions
Loperamide hydrochloride (Imodium) interact with other medications, substances, or conditions, potentially affecting its effectiveness or causing adverse effects. It is essential to understand to these interactions in order to use the product safely and effectively. Here are some key interactions to consider:
Quinidine, Amiodarone, and Other QT Prolonging Agents
- Loperamide prolong the QT interval in the heart’s electrical cycle.
- Concurrent use of medications that also prolong the QT interval (such as quinidine and amiodarone) can increase the risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias.
Macrolide Antibiotics (e.g., Clarithromycin, Erythromycin)
- Macrolide antibiotics can inhibit the metabolism of loperamide, potentially leading to increased loperamide levels in the body.
- This can increase the risk of loperamide-related adverse effects, such as constipation and intestinal blockage.
Antifungal Agents (e.g., Ketoconazole, Itraconazole)
- Like macrolide antibiotics, certain antifungal agents can inhibit the metabolism of loperamide.
- This interaction lead to increased loperamide concentrations and potential adverse effects.
HIV Protease Inhibitors (e.g., Ritonavir)
- Protease inhibitors used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS can inhibit the metabolism of loperamide.
- This increases loperamide levels in the body, potentially leading to adverse effects.
Other Central Nervous System Depressants:
- Loperamide, while generally not crossing the blood-brain barrier in significant amounts, can cause drowsiness and dizziness in some individuals.
- Concurrent use with other medications that have central nervous system depressant effects (such as benzodiazepines, opioids, and alcohol) increases these effects.
Food and Substances:
- Grapefruit Juice: Grapefruit juice can inhibit the metabolism of loperamide, leading to increased blood levels of the drug.
- This interaction enhances the effects of loperamide and increases the risk of adverse effects.
Loperamide Brands in Pakistan
The following are the loperamide hydrochloride brands available in Pakistan, along with the manufacturers:
- Imodium – Aspin Pharma.
- Catadiar
- Diastop
- Direarid
- Emod
- Florame
- Lokit
- Lomide
- Lopamide
- Lopedium
- Lopemid
- Loperam
- Lopim
- Lopra
- Mide .



Leave Your Comment